Go to Xiamen for Appointment - Hubei Xindesheng invites you to gather at the 2026 Xiamen CACLP Exhibition
2026-03-10
Spring and clear scenery, gather strength and move forward. In the current rapidly developing clinical diagnosis and biochemical research industry, every industry event is an important platform for technical exchange, resource docking, and collaborative development. As a backbone enterprise in the field of domestic biochemical raw materials, on the occasion of this industry event, Xindesheng officially announced that it will showcase its core products at the 2026 Xiamen CACLP exhibition. We sincerely invite industry colleagues to visit our booth, discuss industry trends, explore new cooperation opportunities, and embark on a new journey of domestic biochemical raw material development.
The grand industry event has begun, and we have made an appointment to go to Xiamen together
As a highly influential industry exhibition in the field of in vitro diagnostics in China, CACLP brings together core forces such as diagnostic reagent companies, research institutions, distributors, and terminal medical institutions from around the world. It is an important window to showcase cutting-edge technologies, connect with high-quality resources, and gain insights into market trends. Every CACLP exhibition attracts countless industry professionals to gather together, exchange the latest technological achievements, explore industry development pain points, explore potential cooperation opportunities, and promote high-quality development of the in vitro diagnostic industry.
In 2026, the CACLP exhibition will be held at the Xiamen International Expo Center, officially opening on March 21 and continuing until March 23, presenting a comprehensive industry feast covering technology, products, and services. To ensure the smooth operation of the exhibition, Xindesheng attaches great importance to it. Not only did it bring the company's core products, but it also prepared a professional technical team to provide professional explanations, product demonstrations, and demand matching services for visiting colleagues throughout the process. We strive to ensure that every friend who visits the booth can gain something and be inspired.
Direct access to booth information, no getting lost during appointments
For the convenience of colleagues in the industry to quickly find the New Desheng booth and efficiently carry out communication and docking, the relevant information of this CACLP exhibition and the details of the New Desheng booth are now provided in detail as follows. It is recommended that you save them for future use:
Core Time of the Exhibition: The exhibition setup will take place on Friday, March 20, 2026 from 8:30 to 18:00, the exhibition will run from March 21, 2026 to March 23, 2026, and the exhibition will be cancelled at 4:00 pm on March 23, 2026; Exhibition address: Xiamen International Expo Center; Hubei Xindesheng booth number: 4-A3012 (Hall 4).
Xiamen International Expo Center has convenient transportation and complete supporting facilities. Colleagues can take public transportation or drive to the exhibition site. After arriving at the exhibition site, they can directly go to Hall 4 and quickly find booth 4-A3012 according to the booth number. All exhibitors of Xindesheng will warmly welcome your arrival and have face-to-face communication and discussion with you.
Core products debut, unlocking new advantages of domestic substitution
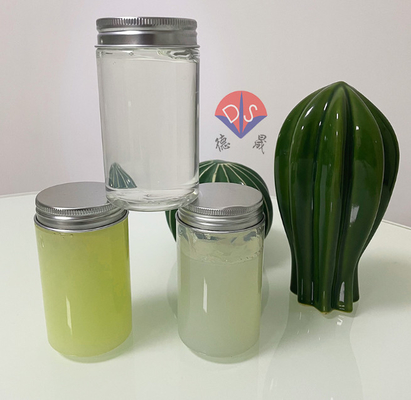
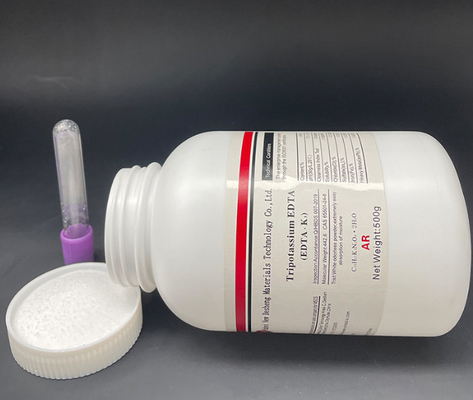
Core products: Hubei Xindesheng Materials will showcase the company's core products at booth (4-A0003). As for the blood collection tube additive series, products such as serum separation gel, heparin lithium, heparin sodium, EDTA dipotassium/tripotassium/disodium, coagulant, coagulant powder, etc. will be displayed in sequence. Biological buffering agents will display products such as TRIS, HEPES, MOPS, CAPS, TAPS, etc.
Newly invested enzyme preparation products: The company has established an enzyme preparation project team since 2024. At this exhibition, the company will showcase enzyme preparation related products at the CACLP exhibition. Our technical team will explain the characteristics and applications of the products in detail on site and provide professional solutions.
On site, the technical team of New Desheng will provide a detailed explanation of the production process, performance advantages, and application scenarios of the product to colleagues. They will also demonstrate the effectiveness of the product and provide professional solutions to the problems encountered in practical applications. Whether you want to understand product parameters, explore innovative applications of products in clinical diagnosis and biochemical research, or seek long-term stable partners, you can find answers at the New Desheng booth.
Inviting colleagues to gather and explore the new future of the industry together
The CACLP exhibition is not only a platform to showcase the strength of enterprises, but also a bridge for industry colleagues to exchange and cooperate. During this exhibition, Xindesheng not only hopes to showcase domestic in vitro diagnostic products to the industry, but also hopes to use this platform to have in-depth exchanges with industry colleagues, listen to industry needs, explore industry development pain points and future trends, seek more opportunities for cooperation, and work together to promote high-quality development in the fields of in vitro diagnostics and biochemical research.
In March, Xiamen, with warm spring and blooming flowers, the grand event begins and we embark on a new journey together. Hubei new desheng is fully prepared and is waiting for industry colleagues to arrive at booth 4-A3012 in Hall 4 of Xiamen International Expo Center. Together, we will explore new directions for industry development and build a new future for the development of domestic biochemical raw materials! Looking forward to meeting you in Xiamen, living up to our encounter, and together we will embark on a beautiful journey!
Read More

 Your message must be between 20-3,000 characters!
Your message must be between 20-3,000 characters! Please check your E-mail!
Please check your E-mail!  Your message must be between 20-3,000 characters!
Your message must be between 20-3,000 characters! Please check your E-mail!
Please check your E-mail!